- 21 July, 2021
- Rebeca Gallego
- Comment: 0
- Projects

PHOTOVOLTAIC PLANT DESIGN IN SPAIN
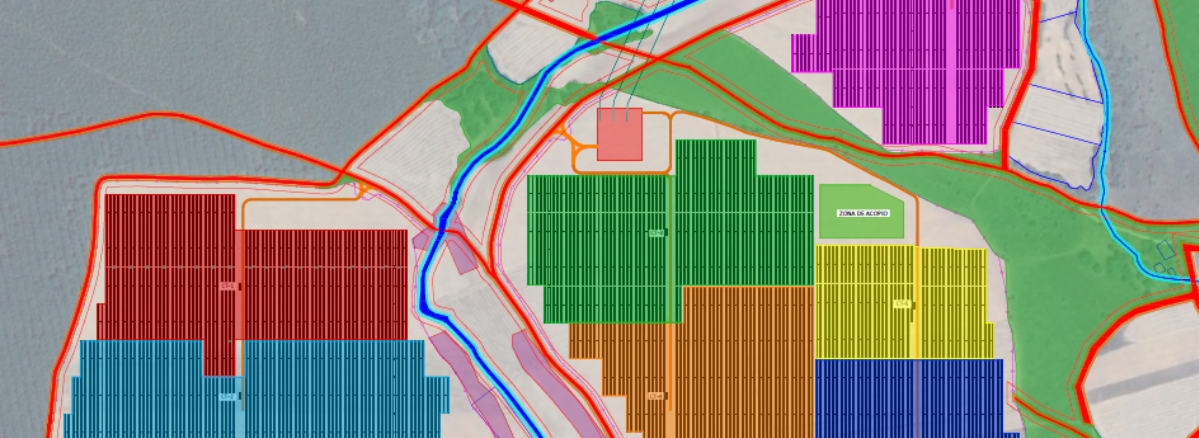
We are currently working on the basic design of a 50 MWp photovoltaic installation in Villota del Páramo (Palencia). This installation will have polycrystalline photovoltaic panels, installed on mobile structures with tracking on one axis.
The design of a photovoltaic plant begins with a study of the terrain on which the implementation is carried out, thus making a distribution of the panels to achieve a desired peak power. Subsequently, the series grouping of the panels is studied according to the requirements of the selected inverter, as well as the number of parallel groupings for each inverter input.
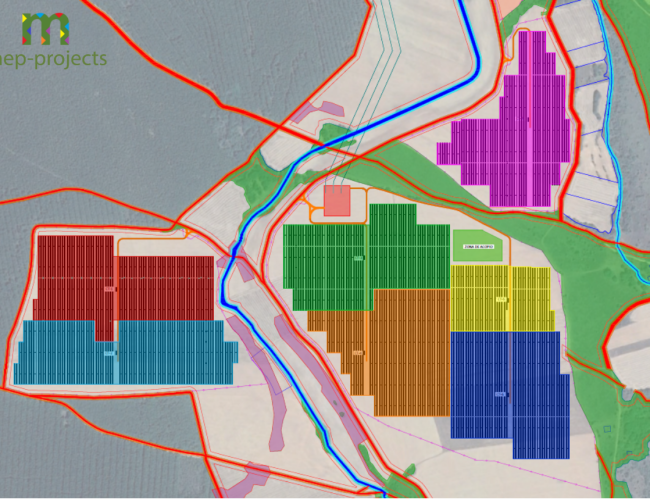
Figure 1. Photovoltaic Plant Configuration
In this case, we have connected 28 or 29 panels in series, forming what is called a loop or “string”. These strings are then grouped, depending on the arrangement, in 8, 10, 12 or 16 strings in parallel. This calculation of the distribution of the panels and strings throughout the plant is carried out so that the load of the inverters is as well compensated as possible.
Once the plant configuration has been selected, the low voltage solar wiring is calculated. After this calculation, the configuration used is checked for correctness. The low voltage wiring is divided into different types:
- Solar cable (light blue): this is the outgoing cable from a string or ring, up to the junction point with other strings. It is also called patch cords.
- Bus cable (dark blue): this is the collector cable of the solar cable, to which all the patch cords are connected by means of clamps, up to the grouping sectioning box.
- CC evacuation cable (green): this is the evacuation cable of a string grouping, which runs from each grouping’s isolation box to the inverter, located in the isolation center.
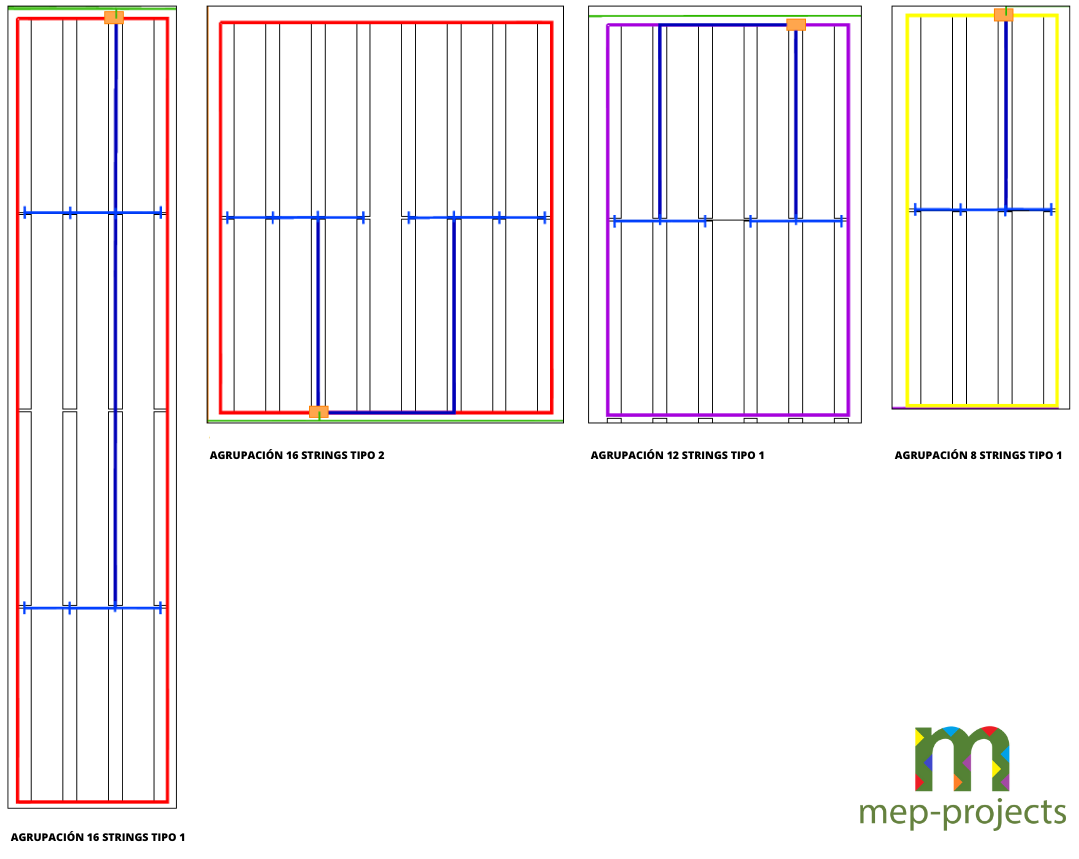
Figure 2. Grouping Configuration Scheme
After choosing the configuration and calculating the wiring of each part of the plant, the medium voltage wiring is calculated. This cable, which is used for the evacuation from the transformer stations, which raise the output voltage of the inverter to medium voltage, runs through the plant in a ring between the different transformer stations, until it reaches an elevator substation.
Once the wiring calculation has been made, the conduits to be used for the different cables are studied:
- Directly buried for the medium voltage cable (green).
- Directly buried for the DC evacuation cable (pink)
- Overhead (aerial) for the solar cable and bus cable.
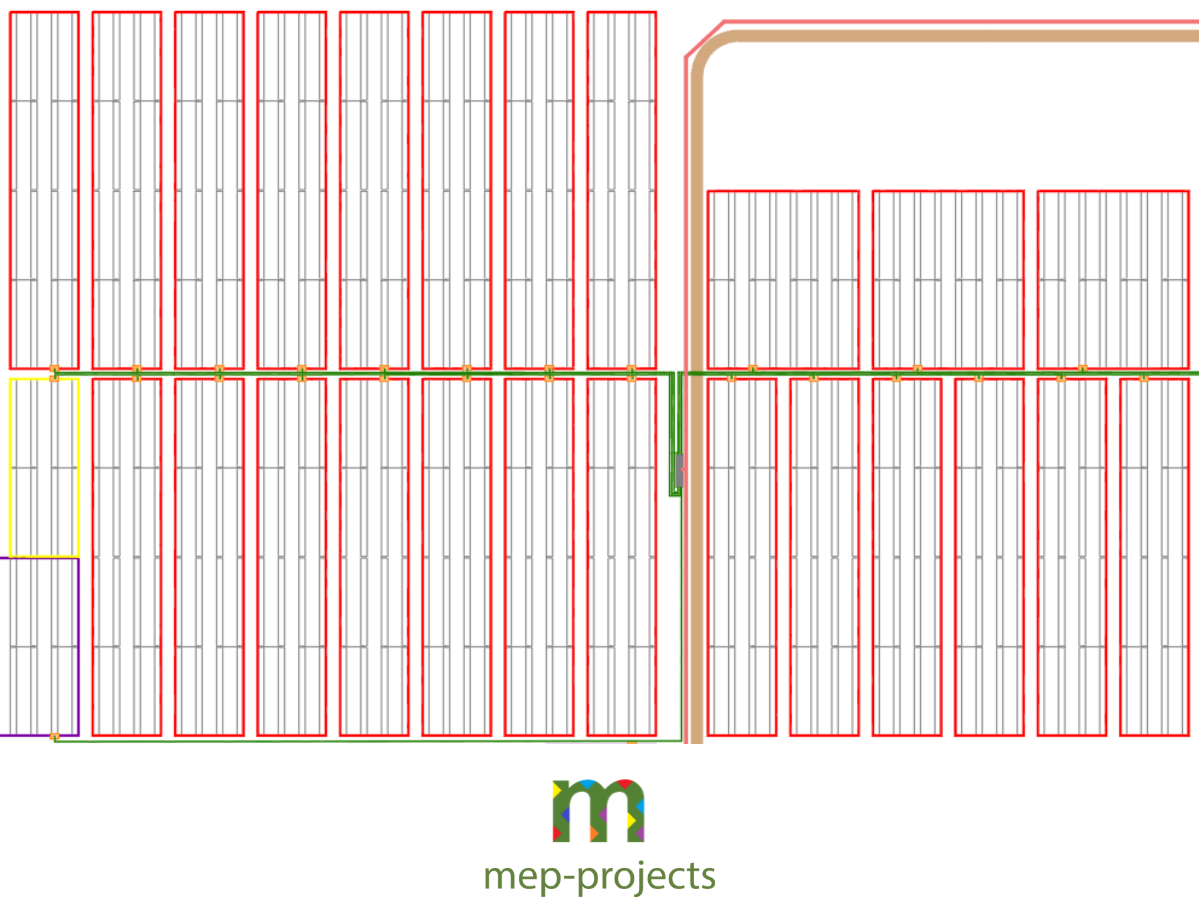
Figure 3. Cunfiguration cable ducts of LV and MV