- 11 March, 2024
- Francisco Gallego
- Comment: 0
- News

REUSE OF POTABILIZED WATER FOR GREEN HYDROGEN PRODUCTION PROCESSES
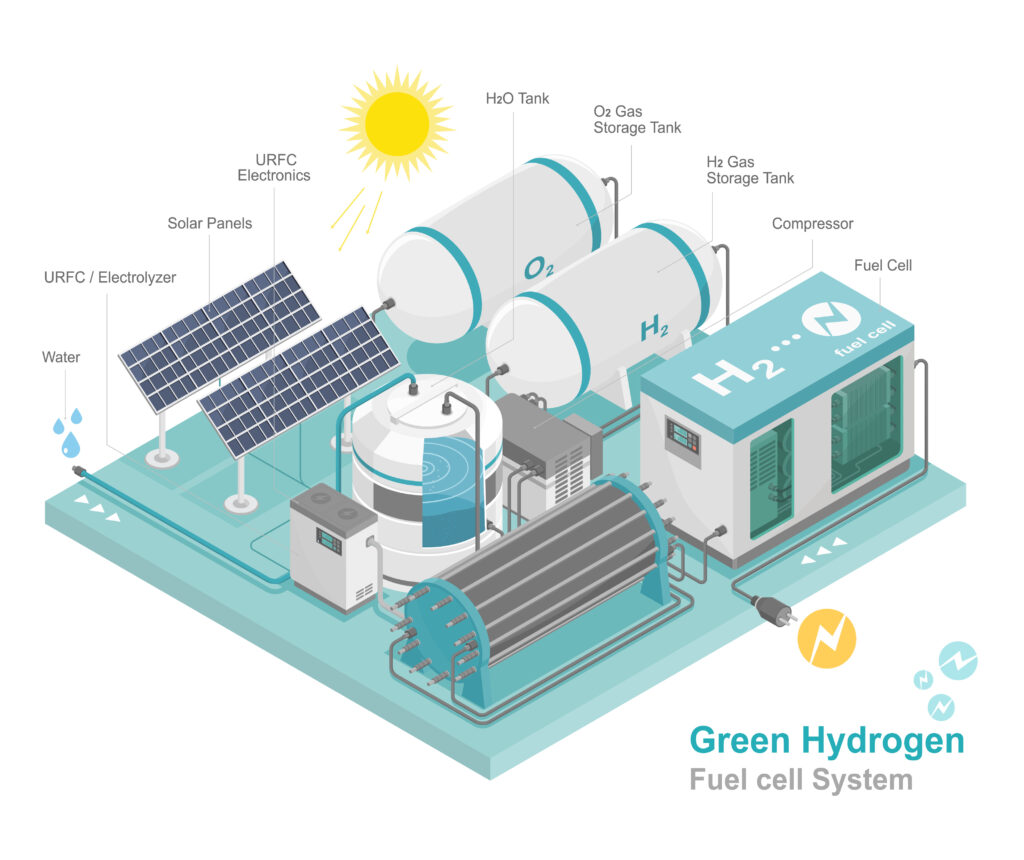
In the current landscape of transitioning to renewable energy sources, the role of green hydrogen as a fuel has become pivotal. This resource not only meets the growing energy demands but also provides a clean and efficient long-term solution, marking a milestone in the evolution toward a more sustainable energy. In this context, MEP-Projects stands out as a specialized technical office in the green hydrogen auxiliary industry, playing a crucial role in the development of related projects.
According to 2019 data from the DGT (General Directorate of Traffic), there were 10,9 million gasoline and 13,5 million diesel cars circulating in Spain. Let’s imagine that all these vehicles ran on green hydrogen (H2), covering an average of 15.000 km per year. The water requirements to produce green hydrogen would be significant but manageable. Assuming 0,9 kg of H2 every 100 km and 18.000 liters of water for one ton of H2, approximately 59,29 hm3 of clean water would be needed for the Spanish vehicle fleet’s mobility in a year.
This quantity wouldn’t be restrictive compared to other water needs in Spain. For instance, it would be equivalent to the irrigation needs of 9.121 hectares with an allocation of 6.500 m3/ha or the urban consumption of a city with 653.041 inhabitants using 250 liters per person per day. However, the Spanish hydrographic reserve, shown in Illustration 1, is currently at 51% of its total capacity, exacerbated by the drought state of emergency in the southern and Mediterranean coastal areas.
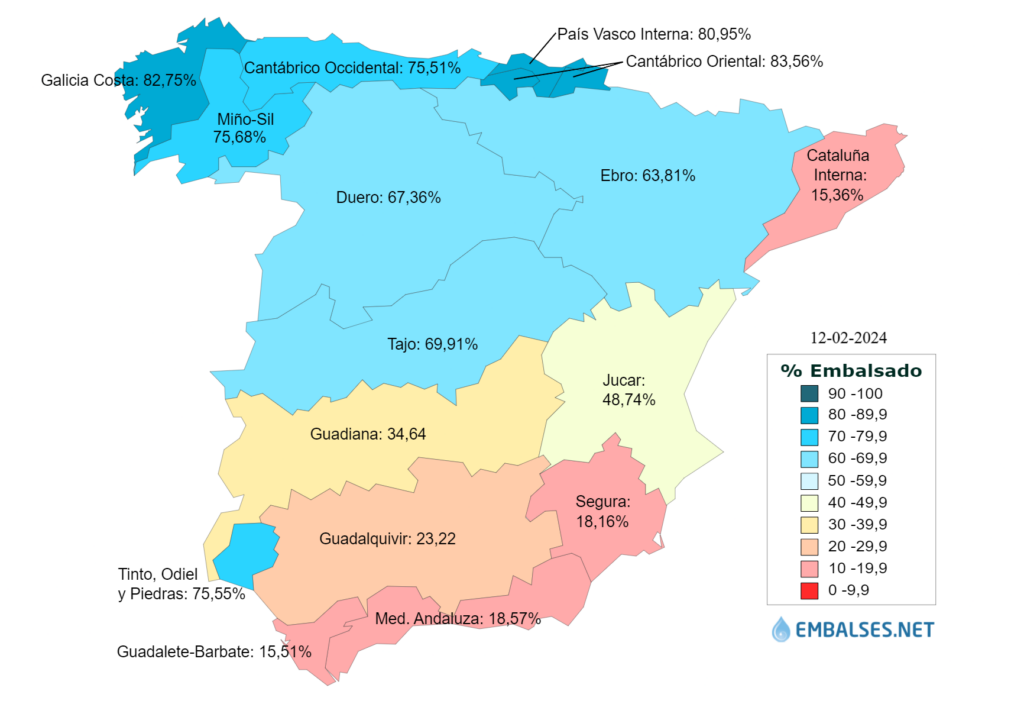
Illustration 1. Total capacity of basins as of February 2024.
In this situation, the reuse of potable water, especially from seawater, emerges as an essential alternative for green hydrogen production. Freshwater, both surface and underground, has become a scarce and valuable resource that we must preserve.
The reuse of potabilized water for green hydrogen production processes offers several advantages, both from an environmental and economic perspective. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Conservation of water resources, reducing the demand for fresh water, contributing to the preservation of water resources, especially in water-scarce regions.
- Environmental sustainability. Using potabilized water reduces pressure on natural water sources, such as rivers and lakes, preserving aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Cost reduction. Utilizing potabilized water can lead to significant savings for industries producing green hydrogen by reducing the need for additional water treatment.
- Lower carbon footprint. By reducing the demand for fresh water and associated treatment processes, a decrease in the carbon footprint of green hydrogen production can be achieved.
- Supply security. Reusing potabilized water can help ensure a consistent water supply for industrial processes, even in drought or water scarcity situations.
- Corporate social responsibility. Adopting sustainable practices, like water reuse, can enhance companies’ image and reputation by demonstrating their commitment to social and environmental responsibility.
- Promotion of circular economy. Water reuse is part of a circular economy approach, where resources are used more efficiently, and waste is reduced, contributing to a more sustainable system.
It is crucial to consider regional specificities, water quality, and technical requirements when implementing water reuse for green hydrogen production. In this context, MEP-Projects stands out as a strategic engineering partner, offering advanced solutions for cutting-edge projects.
If you are interested in seawater desalination, hydrographic efficiency, or other related topics, we invite you to start a conversation with us. We are committed to sharing our knowledge and developing customized solutions that precisely address your challenges and ambitions.
Made by Fco. Javier Marín (EICA Design Engineer)

